Created by Ameyah Official
overview to the lectures on Modulation and Simulation
Auf der 2. Tafel mit der Berechnung der Gewichte ist mir
beim Gewicht c_{2,2} ein eigentlich auffälliger Schreibfehlerunterlaufen, da der an der Tafel angegebene Wert 64/65 erstens
nicht > 1 ist, zweitens nicht das Produkt von 15 und 3 als
Nenner enthält und drittens nach der allgemeinen Formel für c_{m,m} größer als c_{1,1} = 4/3 sein müsste.
Kurzum: Der richtige Wert ist natürlich c_{2,2} = 64/45 .
Nur so ergibt auch die Summe der Gewichte c_{2,i} den Wert 1 : 1/45 - 4/9 + 64/45 = 1 .
1. Def prob. --> simplification
2. physical prob --> model error
3.Math.modeling --> approx error
4.math. approx --> rounding error
5.computation --> error analysis
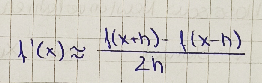
h-balance zw. rundungs und genauigkeit.
Motivation für FPNs und integers
- single 32bit
- double 64bit
-extended 80bit
-quadruple 128bit --> Details später!
program test_epsilon
real :: x = 3.143
real(8) :: y = 2.33
print *, EPSILON(x)
print *, EPSILON(y)
end program test_epsilon
Norm of x\neq 0:
mantissa digits um k-digits nach links schieben (k= anz. führender 0-Ziffern) und subtraktion von k von e_x, then e_xneu = e_x-k
x \neq 0!
x = (s_x, m_x,e_x,b)
Intervallbasierende Räume mit FP und kompatibilität mit Funktionen.
also zb. \sin(X) = [\sin(x_min),\sin(x_min)], this probably changes the order? Periodicy
Only possible if e_xneu = e_x - k \ge e_min
Parallelisierung:
x is a number in R or \R?
B(x) = [x_n-1 x_n-2, ..., x_1, x_0]_2
Value: |B(x)|=\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}x_i \cdot 2i = usigned value of x
https://i.imgur.com/sNO6vIS.jpg
R = R(b,l,e_min,e_max, denorm)
denorm = true, if denorm. FPN are allowed or false otherwise
IR = {X = [x_min,x_max], x_min \le x_max, x_min,x_max \in R}
Interv mit FP Grenzen
e = b(1-l) = 1/bl-1
with l = mantissa length
größte rel. Abstand zw. zwei benachbarten normalisierten FPN ~ größter rel. Fehler bei Rundung
e_x = e_min and mantissa not normalized/normalizable
|B(x)|+ |B(-x)| = 2n-1
|B(x)| +|B(-x)| = 2n
Value in 2er complement of num. a
a = (-) a_n-1 \cdot 2n-1 + \sum_{i=0}^{n-2} a_i \cdot 2i
with (-) wirkliches negative: 1--> -1
2 ganze Zahlen mit je n bit add/sub.
z * = x+/* y with x,y \in I_n (integer with n-bits with incl. Vorzeichen)
ulp(x) = \begin{cases}
be_x-l falls x normal\\
be_min - l falls x denorm oder 0
\end{cases}
unit in the last place at the mantissa of x = Einheit in letzter Stelle
I\R = {X = [x_min,x_max] x_min \le x_max, x_min,x_max \in R}
z := ((z * 2n-1)mod 2n)* 2n-1 \in I_n
&: \R \to \R mit &X = [&x_min,&x_max] \superseteq X =[x_min,x_max]
the rounded interval is always a subset of the
original Interv X?-verify?
Op %: \R \to R (FP raster) with 3 properties
R1: %x = x for all c \in R (projection)
R2:x,y\in \R : x \le y \implies %x \le %y (monotonie)
R3: %(-x) = -%x \forall x \in \R (antisym)
R1 &X = X for all X \in IR
R2 X,Y \in IR: X \subseteq Y => &X \subseteq & Y
R3 &(-X) = -&X, cos \triangle (-x) = -\nabla x, \nabla(-x) = -\triangle x \in \R!!!
to R3 remember: -X = [-x_max,-x_min]
X=[a,b] => -X=[-b,-a]!!!
X + Y = [x_min + y_min, x_max+y_max] and
X - Y = [x_min - y_max, x_max - y_min]
equal to
diam(X\pm Y) = \diam X + \diam Y