BTM Reviews
Created by Arlene Weng

challenges in business analysis
evolution of business analysis
valuable skills for business analysis
- enthusiastic learner
- curious
- creative thinker
- open minded (adaptable)
- empathetic (think from user perspective)
- ethical (trustworthy)
- team player
- problem solver
- good communicator
- active listener
- organized
what is business analysis?
- the practice of enabling change in an enterprise by defining needs and recommending solutions that deliver value to stakeholders
- used to:
- understand the current state of the organization
- to define the future state organization
- to determine the activities required to move from the current state to future state
business analysis activities
BTM Lecture Notes
business analysis
business analysis tools and techniques
What is an information system?
IT refers to: (represent raw technology)
- products (e.g. computers, networks)
- methods (e.g. agile)
- inventions ( e.g. world wide web)
- standards (e.g. internet protocol)
A system is: a group of components that interact to achieve some purpose.
An information system (IS) is: a group of components that interact to produce information.
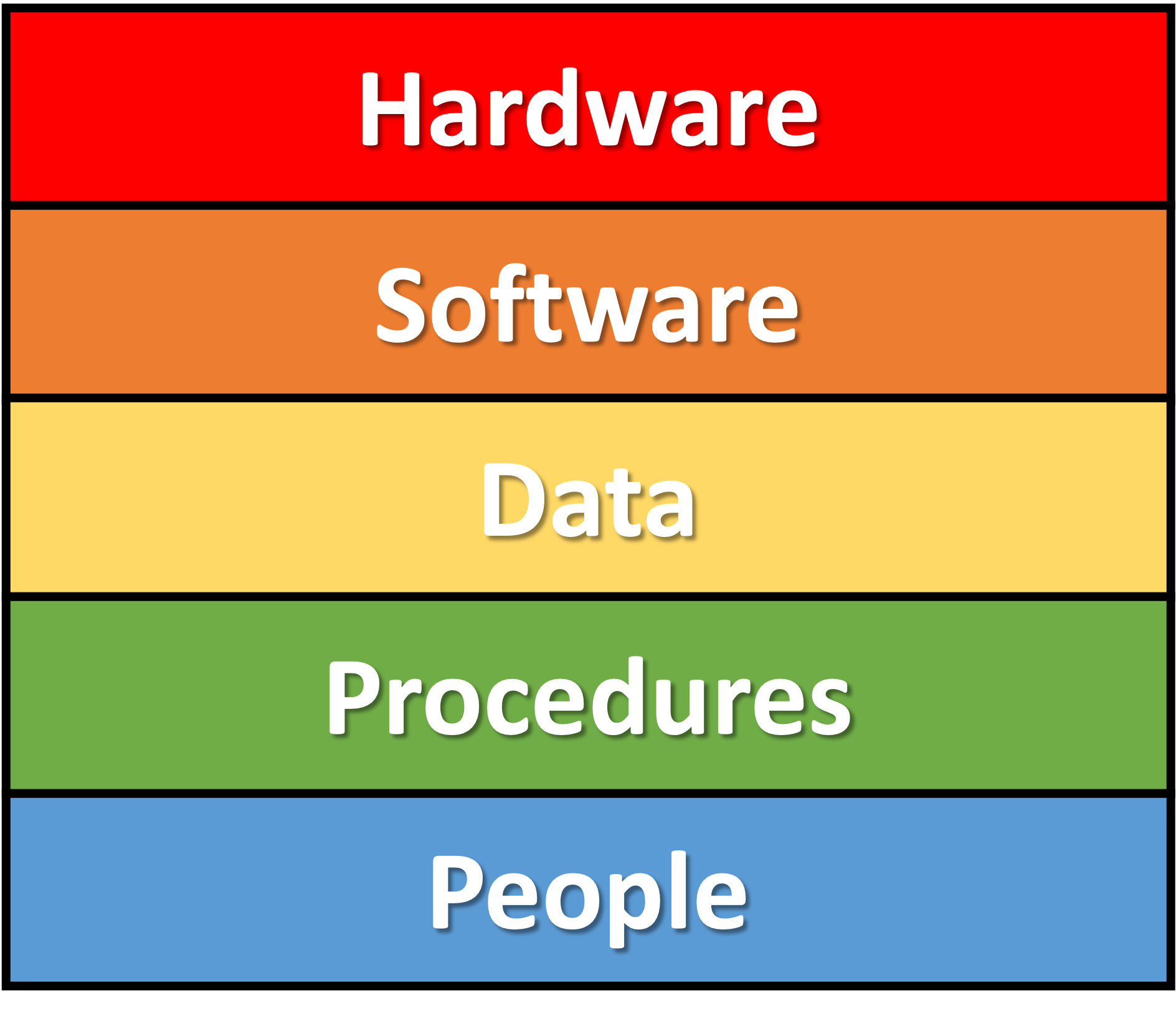
What is data?
- something of value, which can be considered an asset
- can be stored as data, documents, spreadsheets, websites,discussion boards, text from blog, etc.
Database management system (DBMS)
- make db more accessible and useful
- program that creates, processes, and administers a db
Database Design
Business Technologies
What is database?
- organize and keep track of things
- simplifies keeeping track of multiple themes
- single theme - store data in a spreadsheet
- multiple themes - requires database
- e.g. of a theme - student grades, student emails, student office visits, products, customers, warranties, employees, players, games, etc.
databases centralize storage and retrieval of data
- databases consolidate multiple themes of operational data into one integrated, central location.
- operational data are things like payroll records, customer information, and employee data.
benefits of databases
- improved security, and restrict access to databases via user identification, passwords, encryption, etc.
- retrieve information quickly
- enables data integration across the organization
- linking among functions
- sharing information among systems/ function
what does a DBMS do?
3 main functions:
- create the db and its structures
- tables and relationships
- documents the structure in a data dictionary
- process the db
- create, read, update, or delete data
- uses structured query language (SQL)
- provide tools to administer the db
- create/remove users, backup, restore
Entity relationship diagram (ERD)
- serves as the blueprint for implementing the physical data model using DBMS
- entities become tables
- attributes describe entities and become fields (columns) in tables
- relationships link tables on a common attribute or "key" and become formal constraints
Levels of data modelling
- focus is on the relational data model design
- 3 levels of data models:
- conceptual data model - identifies business concepts
- logical data model - defines the data structure and how it is logically interconnected
- physical data model - describes the DB implementation of the data model
What is data modelling?
- data modelling is: the process of creating a layout of information fields to strcutre and organize data
- a data model is:
- a means to communicate with users about data
- a blueprint for creating a physical implementation of a database
What is online analytic processing (OLAP)?
- while data maybe collected in OLTP, the data may not be used to improve decision making
- OLAP system focus on making OLTP-collected data useful for decision making
- OLAP reports can be referred to as "cubes"
- OLAP provides the ability to sum, count, average, and perform other simple arithmetic operations on groups of data
- OLAP report has measures, orfacts, and dimensions
What is online transaction processing (OLTP)?
Transaction processing
- real time processing
- transactions are entered and processed immediately upon entry
- e.g. airline reservation systems, banking systems
- batch processing
- system waits until it has a batch of transactions before the data are processed and the information is updated
- e.g. transfer of all daily branch transaction to the central office for processing
OLTP
- OLTP system collects data electronically and process the transactions online
- OLTP systems support decision making by providing the raw information about transactions and status for an organization
data dictionary (DB assignment)
- DB are self-describing
- collection of integrated records
- contains, within itself, a description of its contents
- metadata
- data that describe data
- makes db more useful than spreadsheets
- makes db easier to use
Benefits of business analytics
- get deeper insight in business
- enhance team sharing and collaboration
- improve productivity and efficiency
- improve customer service and satisfaction
- imformed decision making
- enforce regulatory compliance
- analyze data in a business meaningful way
- increase flexibility and agility
- optimize cashflow and increase profitability
- streamline budgeting and planning
Physical data model
- DB is: a collection of integrated records structured into tables, relationships, and metadata
- physical implementation of the logical data model using the DBMS
- contains a hierarchy of data elements:
- byte is a character of data
- bytes are grouped into columns/fields
- columns grouped into rows/records
- rows are grouped into tables/files
Data modelling term
- entity - a class of real world themes having common attributes (nouns)
- e.g. artist, song, album, genre
- attribute - a characteristic or property of an entity (adjectives)
- e.g. name, year, track length
- relationship - anassociation between 2 or more entities (verbs)
- e.g. artist records songs, albums collect songs, album are a type of genre
- instance - single occurrence of an entity
- e.g. Beatles, Abbey Road, Rock
Data modelling steps
- identify all entities (conceptual)
- identify primay keys (logical)
- identify all relationsjips using foreign keys (logical)
- resolve any many to many relationships (logical)
- determine entity volumes (logical)
- identify attributes (logical)
- implement data model (physical)
Logical Data model
- contains more detail
- defines:
- entities AND their attributes
- constraints (primary key)
- data type of evey attribute
- relationships AND cardinality
- delivered as an entity relationship diagram (ERD)
Conceptual data model
- defines what information is important, how basic concepts are defined, and how these themes are related with each other
- only documents entities and the relationship amongst them
1. identifying entities
3 properties that can be used to help identity entities
- an entity represents a collection or set of "things"
- a set might tangible or abstract - e.g. students, orders, opportunities, products, etc.
- an entity usually represent collections or set of "things" that are of interest to the organization
- an organization have demonstrated willingness to spend time and money tracking the entire set and each individual memebers of the set of "things"
- each entity must have a unique name
- e.g. customer, employee, student, course, section, album, genre, country, province, etc.
2. Primary keys (PK)
- each entity should have an attribute that is a persistent, unique identifier - called the primary key - that can uniquely identify an instance of the entity
- instance - single occurrence of an entity. e.g. ONE student, ONE customer
- PK characteristics:
- unique - no duplicates allowed (i.e. key values cannot be repeated, student ID)
- mandatory - the PK must have a value, cannot be blank (empty, null)
- only one PK per entity - there can only be one PK
- pk can be composed of multiple attributes - called a composite PK
Composite PK
- the term "composite PK" can be broken into 2 components:
- composit - means a combination of multiple components
- PK - means an attribute that can uniquely identify a single instance of an entity
- creating a composite PK:
- a composite PK is a PK formed by combining 1 or more attributes in an entity
- the attributes may or may not unqiuely identify the instances of the entity individually
- when combined, the attributes becomes a PK and can uniquely identify an instance of an entity
3. identify relationship using FK
- the mandatory characteristic (constraint) of the PK is not required
- FK do not have to contain a value (i.e. they can be "empty")
- the name of the FK does not have to match the name of the PK
- the data type of FK must be the same as the PK
Relationships
- created between a "parent" and "child" entity
- PK is in the "one" or "parent" entity
- FK is the parents' PK "installed" in the "many" or "child" entity
self-referencing relationships
- are often used to model hierarchies as an org chart (manager - employees), a social network (user - friends),etc.
6. attribute (facts)
- attributes cannot have the same name within the same entity
- attributes can have the same if they are in different entities
- all instances of an entity have the same attributes