Every Thing I Know About Python
Created by suraj ghalley
Arthimetic Operator
presedent of operator
- () Paranthesis
- ** Exponential R to L
- *Multiplication, / Division, % Modulus, // Floor L to R
- +Addition, -Subtraction L to R
Logical Operator
- and-all the condition should be true to gat true
- or- getting only one condition true is enought to get output true
- not-
Bit Wise Operator
- & and
- | or
- ^ Xor
- ~compliment
- >>right shift
- <<left shift
- working of these operator are provided in given file
 #BitWise Operator.py
#BitWise Operator.py
Comperision Operator
(==) equal to
(!=) is not equal to
(>=) is greater than or equal to
(<=) is samller than or equal to
(>) is greater than
(<) is smaller than
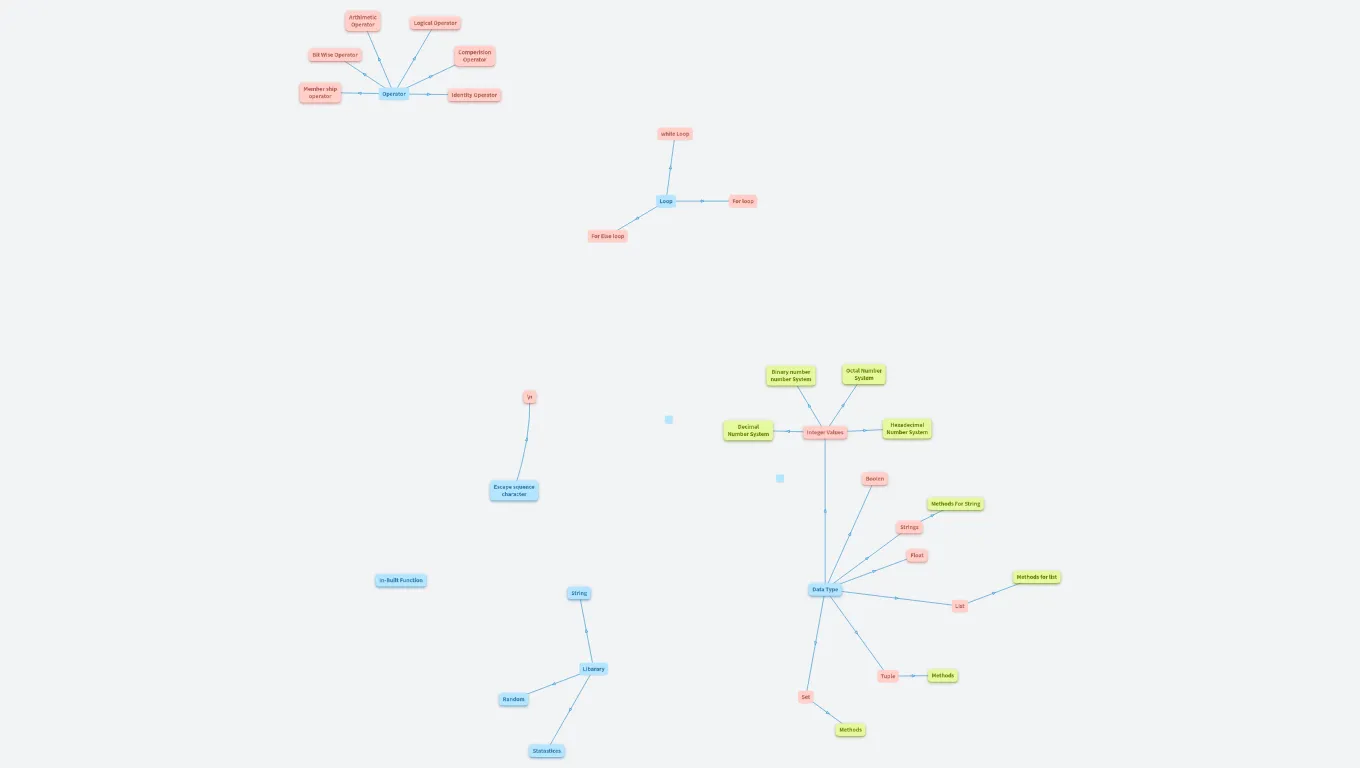
Member ship operator
#True
#False
#False (case sensitive)
Operator
Identity Operator
- is # true if id is true
- is not # true id id is different
while Loop
Loop
For loop
For Else loop
Binary number number System
- Numbers with power of 2
- consist of only 2 character
- 0,1
- print(0b1010)#21
- print(0B1010)#21
Octal Number System
- Numbers with power of 8
- consist of 8 different character
- 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
- print(0o43)#35
- print(0O43)#35
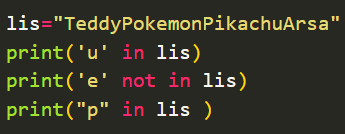
\n
- \n it will move curser in new line
Decimal Number System
- numbers that are in power of 10
- consist of 10 different character
- 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0
Integer Values
All number values that we have learn in math.
Hexadecimal Number System
- number with power of 16
- consist of 16 different character
- 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F
A=10, B=11, C=12, D=13, E=14, F=15
print(0xA7)#167
print(0XA7)#167
Escape squence character
- This character are special tpye of combination of symbols and alphabets that could not be written directly.
- This chatacter are usually written as arguments of print function inside quotation marks.
- combination of character are made by \ and another symbol.
- by using \ we can print all those character that were not able to print directly.
- print("Straw hat's captian \\n \"luffy\" ")###
- ###Straw hat's captian \n "luffy"
- some of this character are:
Boolen
- It consist of only two values
- True and false
Methods For String
split(): helps to divide string valuse base on argument provided
Strings
Example: "Pokemon", "pikachu_1", "369",
'charmander', 'b002saur', '401',
we can perform concatenation, repeatation, indexing,
Float
Decimal number are called as float values
E.G. 0.625, 10.5, 10101110.01101,
In-Built Function
Functions that already defined by creator of python
There are more than 60 pre-defined function.
- dict() - Creates a dictionary.
- float() - Converts a value to a floating-point number.
- id()- Returns memory location id
- input() - Reads a line of input from the user.
- list() - Creates a list.
- len() - Returns the length of argument
- max()- Returns the maximum value from the list
- print() - Prints to the standard output device.
- range() - Returns a sequence of numbers.
- reversed() - Returns a reversed iterator.
- round()- Returns nearest whole number.
- set() - Creates a set.
- str() - Converts a value to a string
- title()- convert into Title Case
- tuple() - Creates a tuple.
- type() - Returns the type of an object.
Data Type
to check data type of variable X
print(type(X))
Methods for list
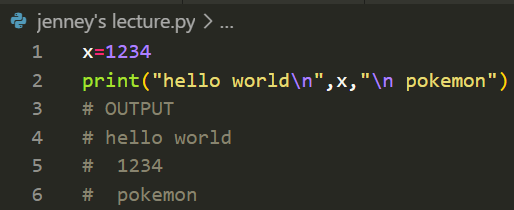
Nested List:
.append():add element at the end
.count(): return the number of provided element
.insert(): add new element at provided index
.pop():remove the ele of given index
.reverse(): reverse the arrangement order
.remove(): remove first occured ele i.e. provided
.sort(): rearrange the elements in assending order
String
it has list of letters, ni=umbers, and symbols too
List
Libarary
Tuple
Methods
.count() return the number of given ele
.index(): return the index of given ele
Random
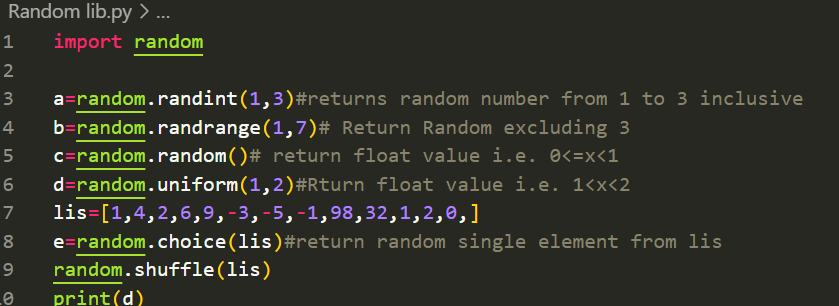
Set
Methods
.add(): its same like append for list
.clear(): delete all ele and makes empty set
.discard(): delete if ele is member
.remove(): delete provided ele
.pop(): delete and return random ele
del set(): delet the exixtence of given set
set1.union(set2) or set1|set2
set1.intersection(set2) set1 & set2
set1.difference(set2) set1-set2
set1.symmetric_difference(set2) set1^set2
set1.symmetric_difference_update(set1)
set1.issubset(set2) set1<=set2
set1.issupperset(set2) set1>=set2
Statastices
Can be used to find mean, median mode and analyse data more