The Hitchhiker's Guide to Fintech
Created by Jakub Liska

Unbalanced Cluster Distribution
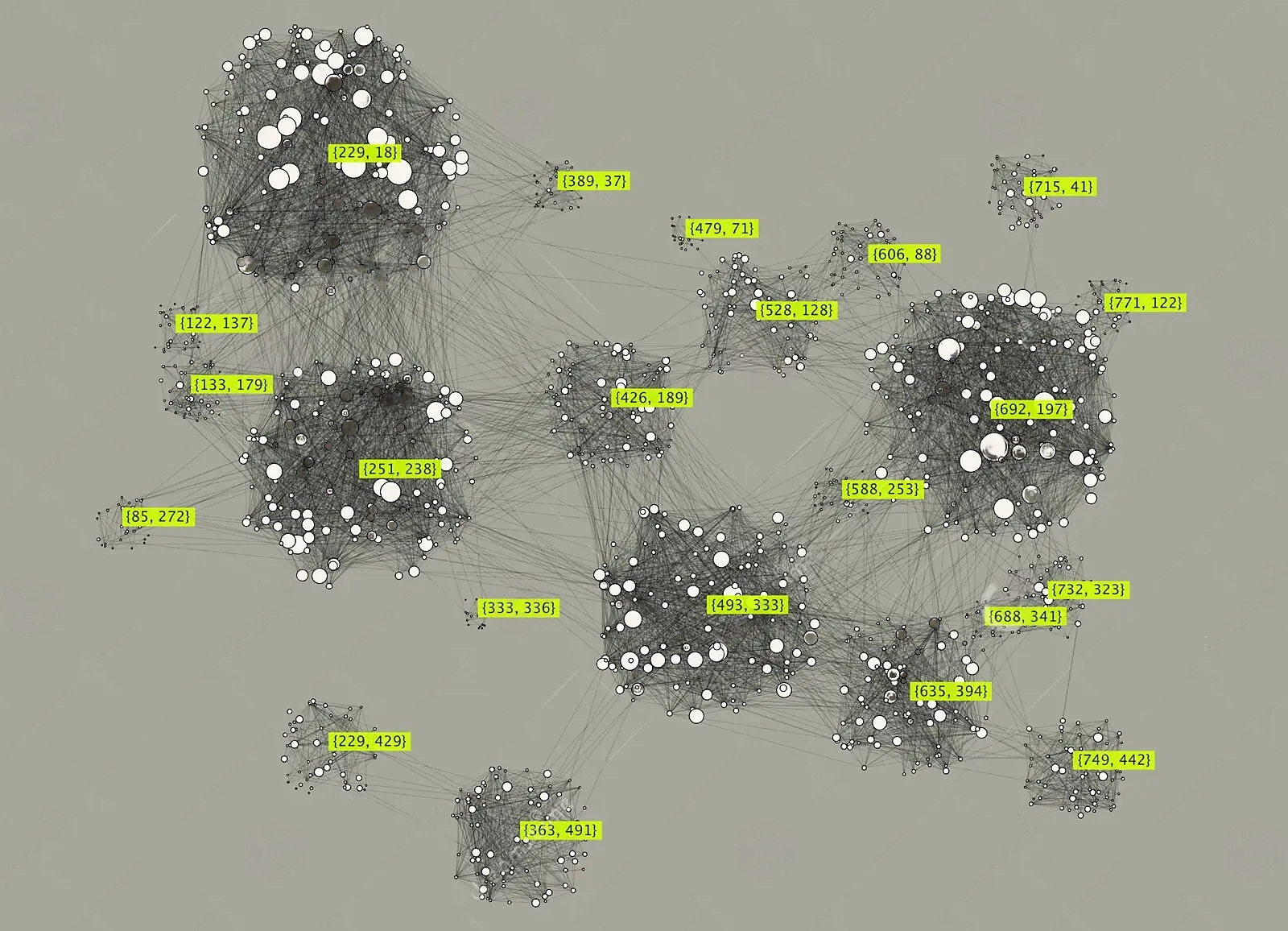
Problem
- Nodes can have different concentration of Whales and Sharks
- pay-for-service transactions
- day trading
⇒ performance issues, bottlenecks, replay time varies, etc.
Solution
- rank-based cluster rebalancing
Centralized vs Decentralized
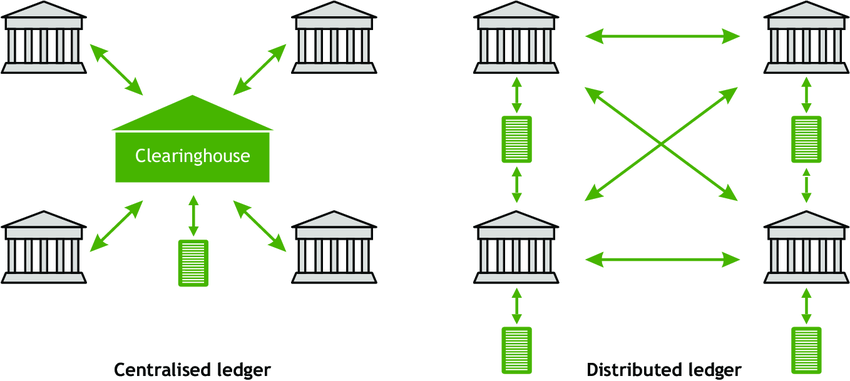
CEFI
Centralized Standards
- Many specifications showed up over time
- ISO20022 - unified messaging format
- FIX - real-time messaging format
- FpML - describes financtial products
- CBPR+ - framework for enhancing cross-border payments developed by CPMI and IOSCO
- ISDA - International Swaps and Derivatives Association
- PCI DSS - security standards designed to ensure that all companies that accept, process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment
Unbalanced Data Distribution
- PostgresSQL : custom DB optimizations / pagination
- Cassandra : hash/time/range partitioning + denormalization
- using Cloud Storages for $ : BigTable / BigQuery
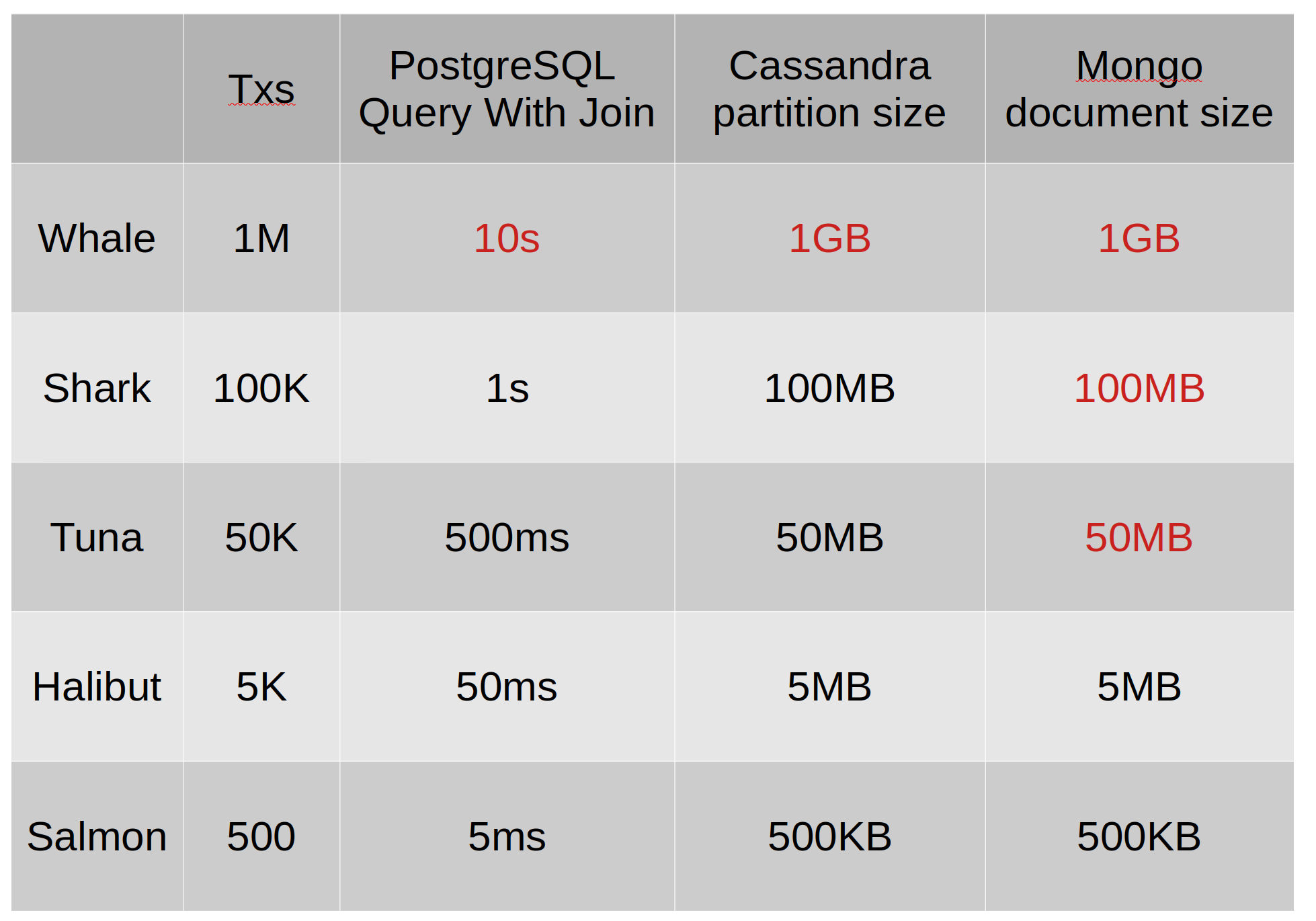
Paradigm shift through analogy
What software reminds me of
- Centralized - totalitarian state and centrally controlled economy
- Decentralized - democratic state and free economy (slightly utopian)
- Hybrid - realistic balance and sustainability
Centralized Banking
WW II (Bretton Woods system): 3 decades of regulation, fixed exchange and interest rates worldwide provided some financial stability
1970s - 2008 : deregulation => massive techno-feudalism and inflation as we know it today
- 1970s : Nixon shock, floating exchange rates, end of gold standard
- 1980s : rise of derivatives, junk bonds, etc.
- 1990s : rise of securitization, subprime mortgages, etc.
2008+ : printing money
- amount of transactions increasing exponentially since Web2.0
Modern Centralized Core Architecture in Scala
- CQRS - Scala/Akka has wonderful framework built-in
- causality principles (action/reaction), FSM
- in-memory State accessible in real-time
- Actors (entities) distributed in shards of nodes in a cluster
- Each actor is being sourced relevant transactions
- building its account balance in-memory (fast-access)
- Each Transaction is used for building general projections
- Projections are part of the design

CQRS (Command-Query-Responsibility-Segregation)
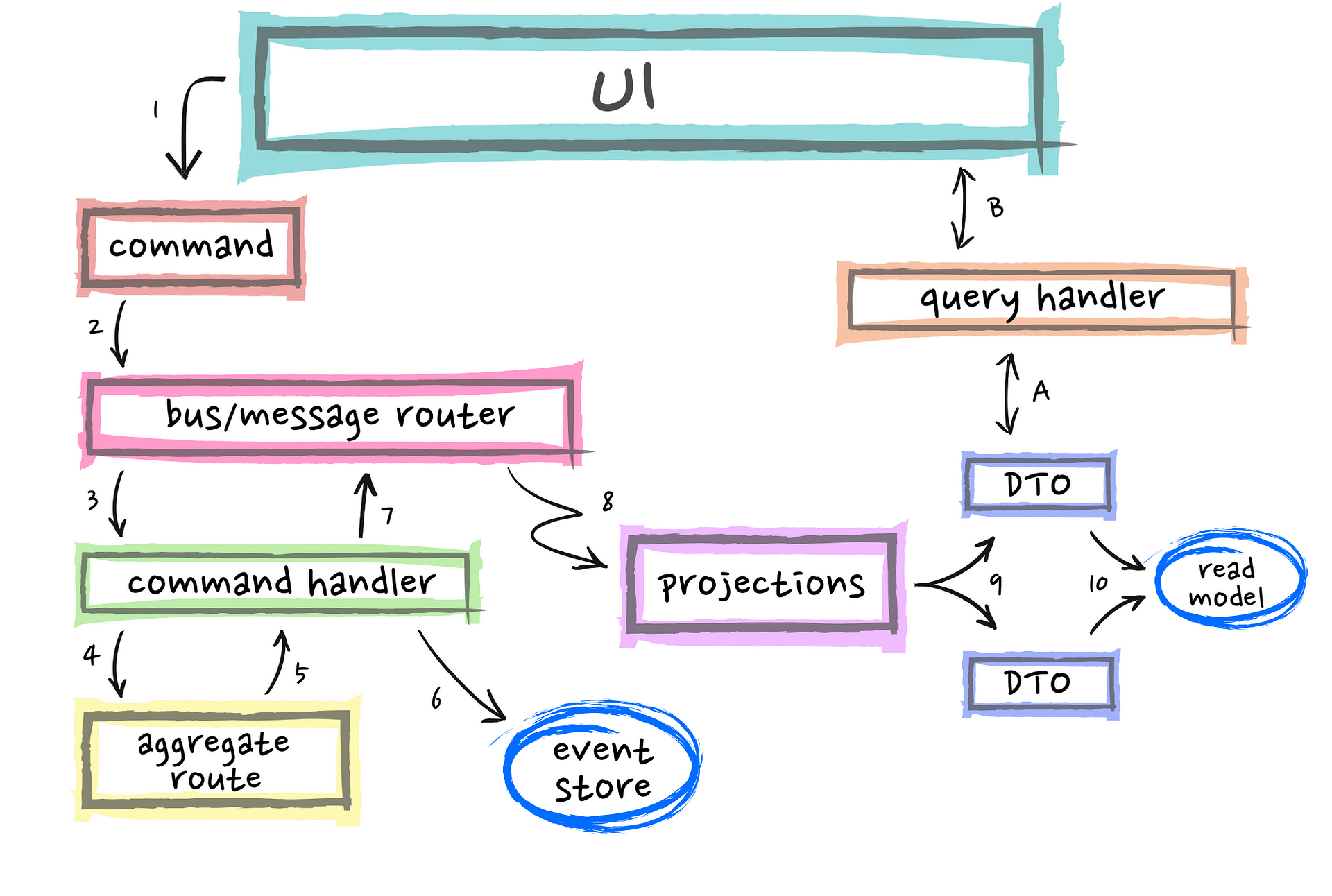
- ideal use-case for distributed Actor System
- centralized on a single cluster
- akka persistence + query
- each actor represents an Account/Entity (in-memory State)
- you are NOT forced to message driven architecture
- Zio Entity (discontinued)
- inspired by Lagom and Aecor (both discontinued)
- EventSourced, EventStore ...
- discontinued or not used much
Centralized problems
- Settlement layer
- complex nightmare causing magic
- finality of Visa Payment Tx (reaching consensus) might take up to 3 days, the payment Fee is ~ 2%
- new parties or banks cannot easily join the centralized system or cluster
- inconsistency
- we rely on database ACID capabilities, write thorough tests with fingers crossed (no cryptographical proofs)
- A lot of State to keep = bad for Functional Programming
- privacy
Shared traits of Centralized & Decentralized worlds
- Settlement between all involved parties
- all parties need to reach concensus about State
- finality = time required to reach consensus
- throughput = how many txs/s
- Event Sourcing - causality based, replayable sequence of action & reaction => quickly accessable State
- Transaction Log => Account Balances
- Transaction is mostly a container of asset transfers between accounts
- Asset = Fiat, anything of value, ownership
- Account represents a balance, a container of assets
- Projections of Transation Log to get better insights
Decentralized Banking
Satoshi Nakamoto
- academia + many years of working in Fintech
- democratized and open-sourced banking
- inspired by decentralized file sharing
2. generation of blockchains
- self-governance : DAO
- general-purpose, rich smart-contracts
- sustainability issues and bottlenecks
3. generation of blockchains
- high throughput, low finality : Solana, Avalanche
- merkle-tree DB replacement of RocksDB
- Relay-chain & Para-chain combination
Decentralized Core Architecture in Scala
- peer-2-peer network and stateless Node are ideal for ZIO
- Blockchain and Projections are separated
- Blockchain = TxLedger + AccountState (zio-chain)
- Projections = Blockchain Explorer (uexplorer)
- TxLedger + AccountState are provably correct and consisent with each other and accross whole p2p network
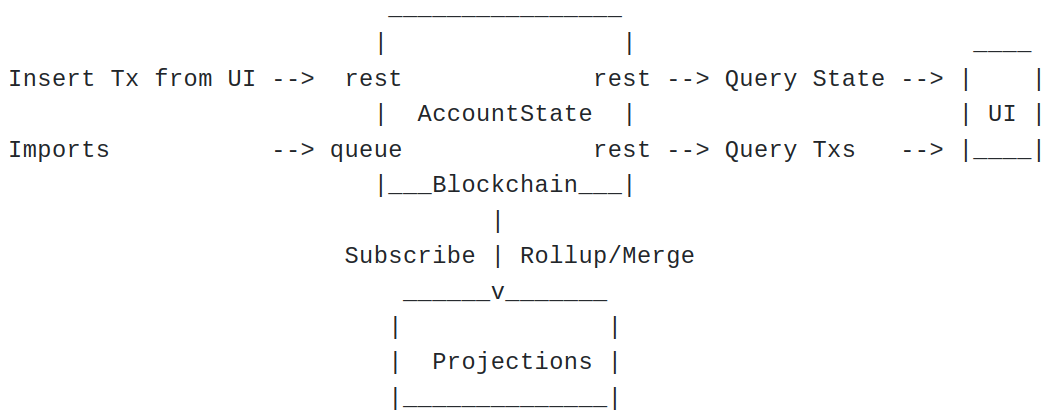
Relay & Para Chains
How sustainability is done? Through further decentralization.
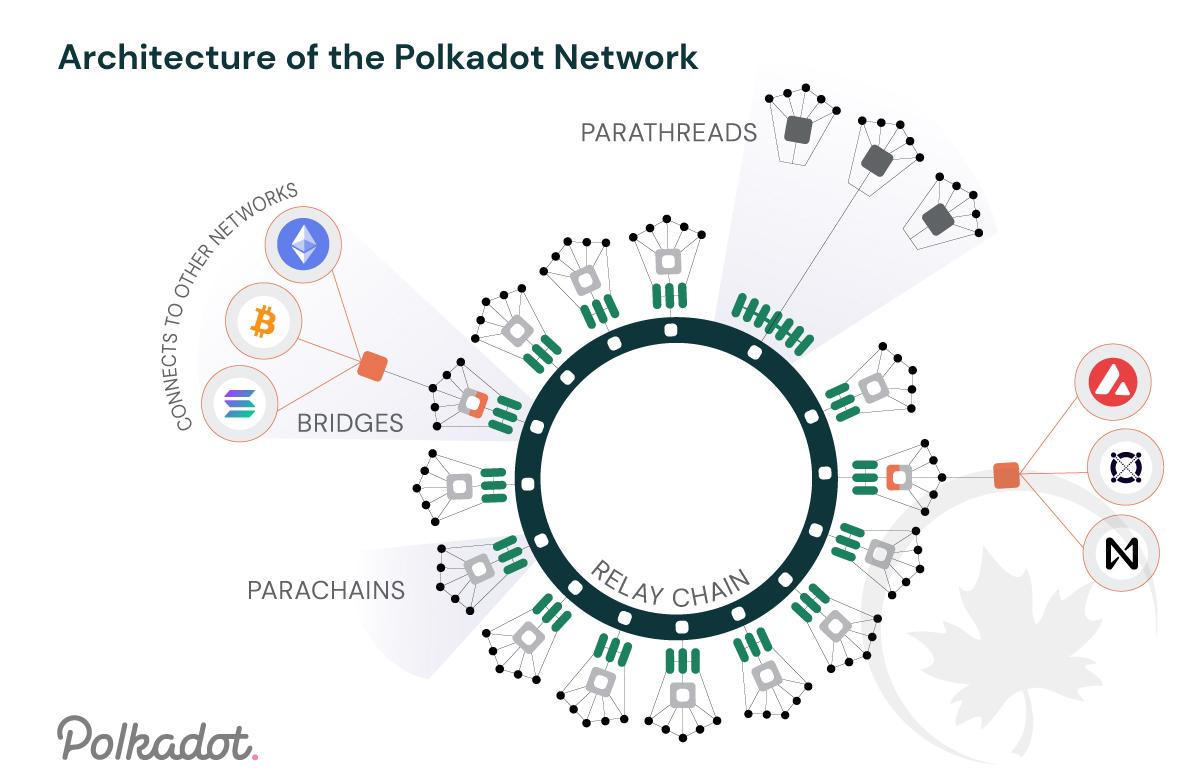
Advantages of decentralization
- Clean standards of Settlement/Consensus layer
- in peer-2-peer network
- any party can join
- good for Functional Programming as only State to keep is Mempool of Txs and Peers
- Fast finality - time required to reach consensus
- consistency - provably correct datastructures
- privacy
Asset Custody - Bridge between centralized and decentralized world
Jakub Liška @ Pragmaxim


Specialization on
- distributed data processing
- blockchains
using mainly
Ideally sustainable, green, meaningful or complexity reducing software that makes the world a better place.
Scala, Akka & ZIO help me to be useful and solve problems which is an opportunity to become even more useful and solve problems better by :
- deeper understanding of some domain like Fintech and transaction processing software
- exploring new domains as people evolve this way and learn to look at the world differently
Decentralized Apps
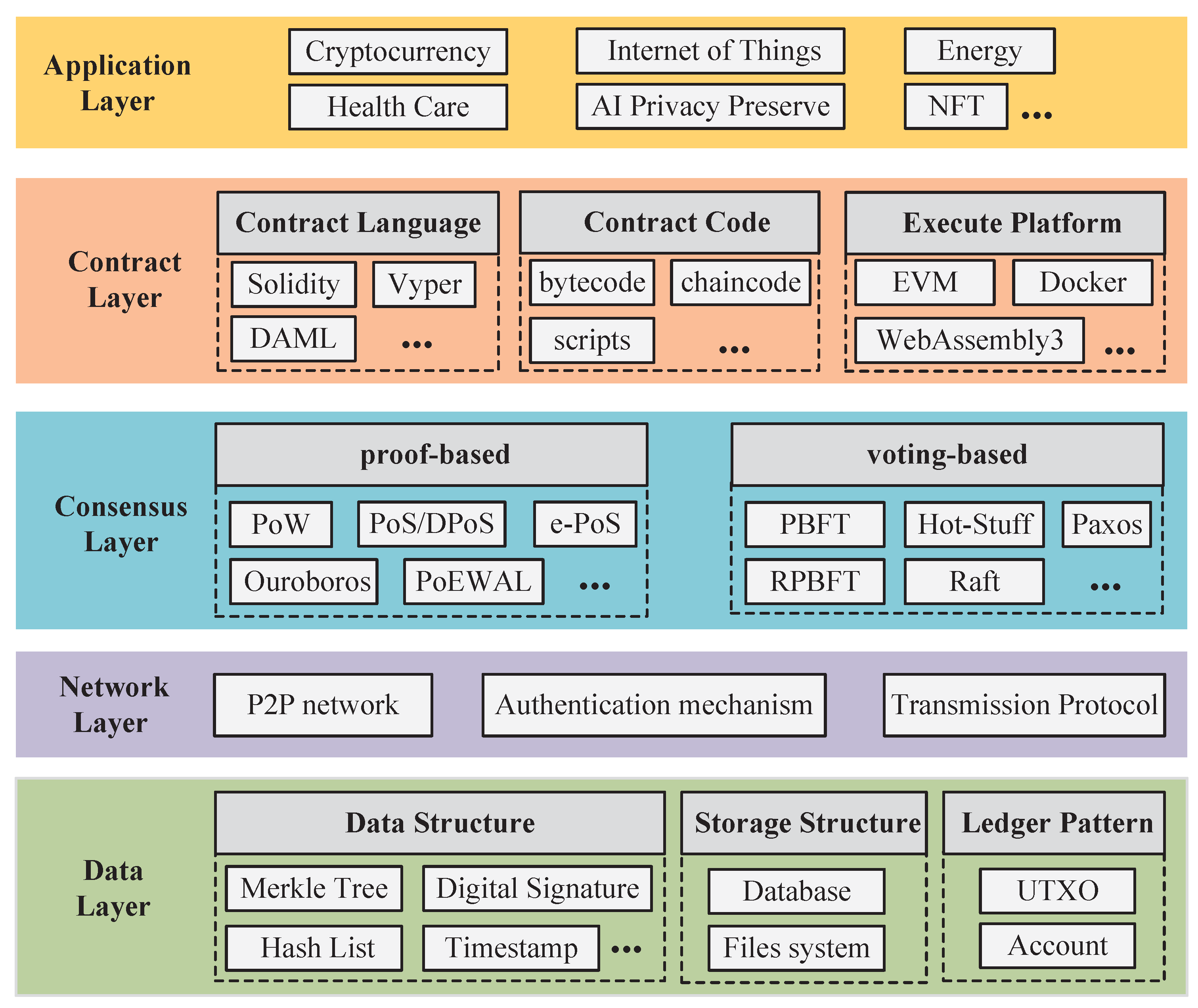
Blockchain Standards
Global, open set of standards reminds of democracy.
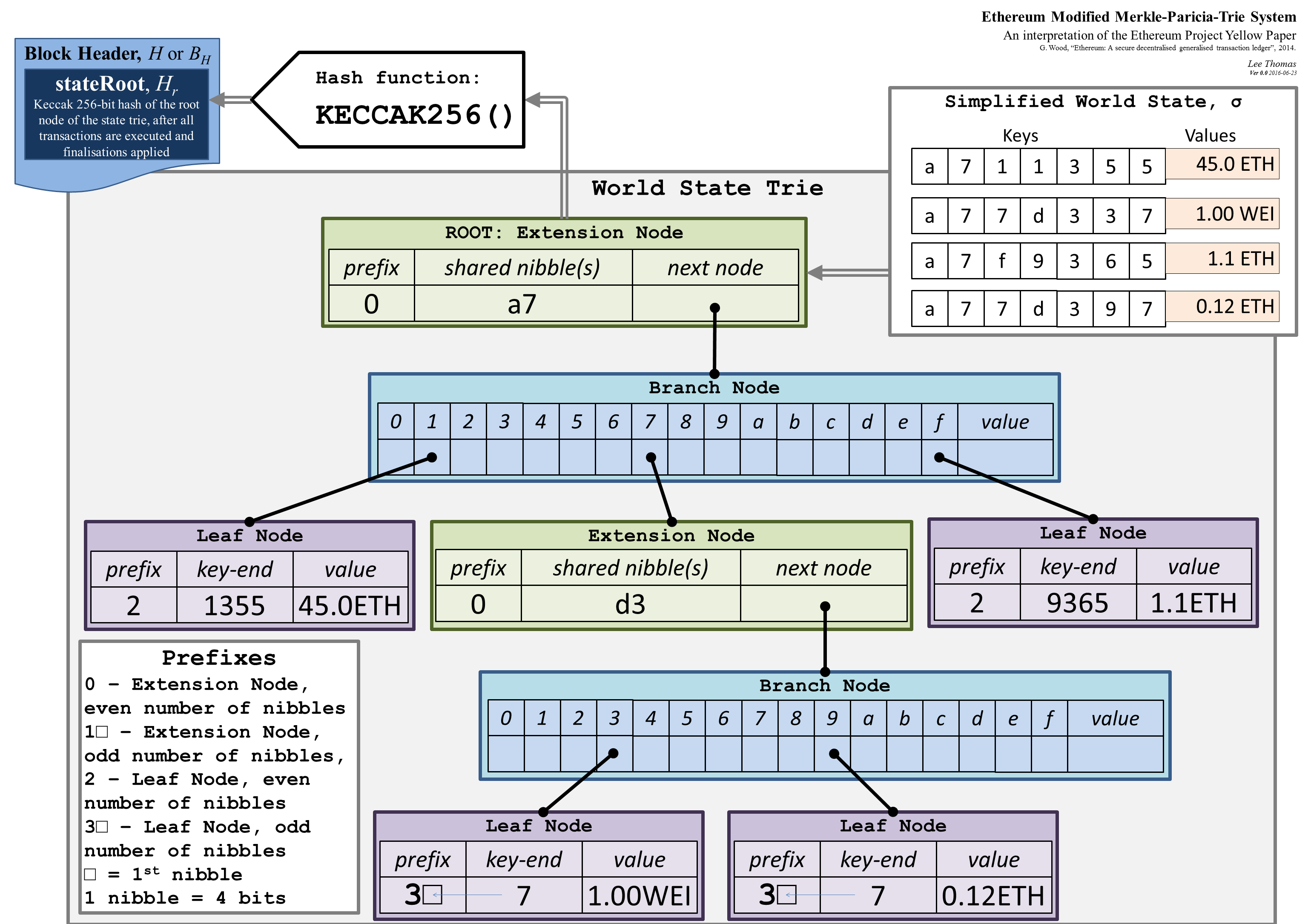
Crypto proofs for fast consensus
- Merkelized Trie Database : Firebase
- Patricia Merkle Trie on RocksDB : Trie-db
- Authenticated Dynamic Dictionaries : AVL+ tree
Blockchain Explorer decentralization
- indexes data and exposes http-api / graphQL
- often provides also analytical insights
- Centralized
- making projections into powerful DB
- hard to incentivize people to run it
- Decentralized : The Graph
- introduced incentivization model
- inversion of control, let index those who need it
- subgraphs of only parts of the chain that are relevant to them
- Indexing blockchain challenges
- handling forks, rollbacks / reverting data
- various transaction formats and assets
- partition size in Cassandra, JOINs in RDBM
